The History of the ISI
"The ISI of the future must be regarded as more embracing than the single society of elected members that we have been in the past … On every hand there is a new dependence upon statistics and statisticians. … There is a crying need for world leadership in this field."
Stuart Rice, President (1947–1953)


The origins of the International Statistical Institute can be traced back to a series of International Statistical Congresses, the first of which was convened by Adolphe Quetelet in 1853 in Brussels.
The ISI was formally founded in 1885, during a meeting held to celebrate the Jubilee of the London Statistical Society.
The initial 81 members were the elite of that era’s statisticians in government and academia.
They established our first statutes, and our first half-century was a period of general stability. Major changes, such as a proposed affiliation in 1920 with the League of Nations, were resisted.
ISI presidents
View all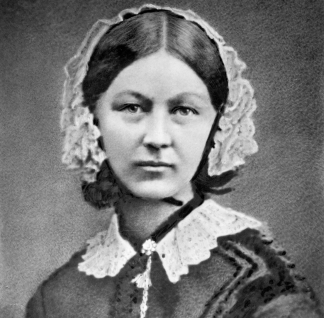
Florence Nightingale & First Achievements
There are several interesting examples of the early development and applications of statistics by ISI members. For example, Florence Nightingale was a pioneer in the development of statistical graphics to visually represent data. She developed diagrams called coxcombs and used them to illustrate the various causes of death during the Crimean War.
In the fourth of the series of articles devoted to the 135th anniversary of the ISI, Jean-Louis Bodin, former ISI President (1999-2001) while describing one of the first achievements of the ISI after its creation in 1885 says: "The first of ISI's objectives led the ISI to prepare and propose international classifications; the first one to come into existence was the International Classification of Diseases and Causes of Death. First discussions about this classification were made during the 1st International Statistical Congress held in Brussels in 1853."
Beginnings of ISI
In June 1885, the Statistical Society of London organised its Golden Jubilee Meeting. The Society was created in 1834, but the Jubilee’s celebration was postponed by one year because of the sudden death of the Duke of Albany, the fourth son of HM the Queen Victoria, on 28 March 1884.

Creation of the ISI in London on 24 June 1885
The creation of the ISI in London on 24 June 1885 was the result of a long history of statistical international cooperation initiated in 1851. The first half of the 19th century saw the birth of many learned statistical societies: e.g., in UK (London, Manchester), in Ireland (Dublin), in USA (Boston where ASA was created in 1839) and in France (Marseilles).

1885 – 1887: From the Creation of the ISI to its 1st Session in Rome
The decisions taken on 24 June 1885 were based on a report proposing possible organisation for the future ISI prepared by Prof Franz von Neumann-Spallart, member of the Imperial Statistical Commission of the Austro-Hungarian Empire and professor of statistics at the University of Vienna, Austria.

The first achievements of the ISI after its creation in 1885
This fourth paper of Jean-Louis Bodein describes some of the first achievements of the ISI.

1885 - 2020: The ISI and its Founding Members
The ISI was established in London on 24 June 1885 during a meeting organised by the presidents of the Statistical Society of London and the Société de Statistique de Paris. During this meeting, 56 members were elected and are therefore considered the pioneers and founders of our Institute.










































